Anycast DNS is used by leading DNS providers such as Netnod to ensure DNS queries can always be answered as quickly as possible. But how does Anycast DNS actually work and why is it important for your domain?
The DNS is often called the phone book of the Internet. It is the system that translates IP addresses into human readable names that you can easily type into your web browser. If we follow this analogy, imagine if there was only one copy of the book in which your website was listed. Anyone who wanted to find your website would first have to travel to where that book was located to get your details. That’s a lot of unnecessary travelling!
Now imagine what would happen if that one book was compromised, damaged or destroyed. Your web presence would continue to exist but no one would be able to find it.
In simple terms, this is the situation you are in if you have just one name server answering queries for your domain. It’s fine for users who are close to that server, but for everyone else, it takes longer for them to be directed to your web presence. In the event of maintenance, a software glitch or a DDoS attack, your domain becomes unreachable.
1. How does Anycast DNS work?
Anycast DNS is a simple and extremely effective way to ensure users can always find your domain. Instead of having just one name server answering DNS queries for your domain, you get multiple instances of that name server distributed all over the world. This means that if one name server is unavailable, the system automatically reroutes DNS queries to another one. Anycast DNS uses intelligent network design to ensure that every DNS query is always answered by the best available name server. When the anycast network has a good global footprint, this guarantees low latency for all users no matter where in the world they connect.
2. How does Anycast DNS help my domain?
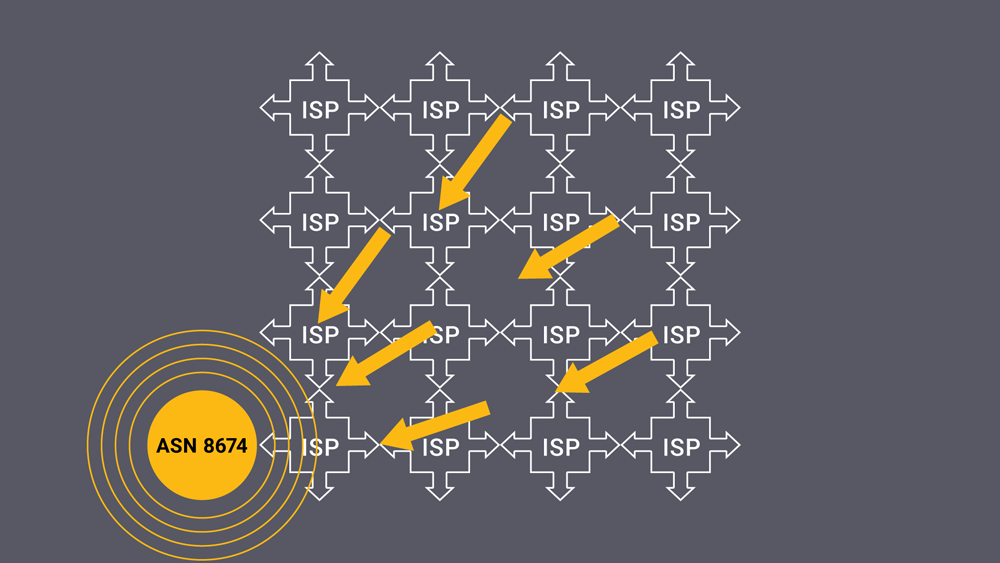
Let’s look at a concrete example of Anycast DNS in action. For this, we will use Netnod’s network which is identified on the Internet using the Autonomous System Number (ASN) 8674. Figure 1 shows the situation if Netnod had only one name server answering DNS queries for Netnod’s domains. This setup is called unicast as there is one server in one location answering all DNS queries. This means that queries coming from further away take longer to be answered. If that server goes down for any reason, either because of a DDoS attack or any kind of outage, the queries for Netnod’s domain won’t be answered. Netnod will still have a presence on the Internet, but users won’t be able to find it.